Information on Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoids are extremely uncomfortable and a very difficult condition to treat. Unfortunately, they are very common. About 75 percent of people will have hemorrhoids at some point in their lives.1 Hemorrhoids are most common among adults ages 45 to 65.2
Too much pressure on the veins in the pelvic and rectal area causes hemorrhoids and they often result from straining to have a bowel movement. Other causal factors may include pregnancy, chronic constipation, or diarrhea and, as we grow older, our chances also increase. Generally, symptoms disappear within several days. However, for many others, this is not the case and further treatment may be needed, even surgery. Once you have suffered with hemorrhoids, not only are they difficult to get rid of in the first place, but it actually increases your likelihood of future occurrences.
What are Hemorrhoids?
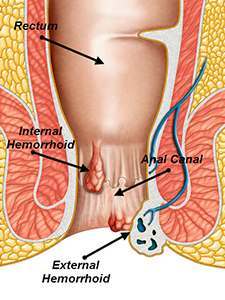 Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins in or around the anus and rectum. These may bleed, itch, and feel outright painful. Hemorrhoids are not typically life threatening, but can cause immense discomfort. They may be completely internal, or may protrude and swell outside of the anus, forming painful bumps. They are common, occurring in both men and women. It's for this reason that a colonoscopy is a standard routine procedure for patients over 50 years old in the United States.
Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins in or around the anus and rectum. These may bleed, itch, and feel outright painful. Hemorrhoids are not typically life threatening, but can cause immense discomfort. They may be completely internal, or may protrude and swell outside of the anus, forming painful bumps. They are common, occurring in both men and women. It's for this reason that a colonoscopy is a standard routine procedure for patients over 50 years old in the United States.
Hemorrhoids are often caused by excessive straining during bowel movements. This may have a variety of causes. Constipation can create particularly hard stools, for instance, which might lead to straining. Pregnancy can also create strain during bowel movements due to the increased pressure on the area due to the baby's weight and shifts in hormones. Diarrhea may also cause hemorrhoid problems.
Furthermore, many people have an inadequate amount of fiber in their diet, which interferes with proper bowel movements and increases the likelihood of hemorrhoids.
There is no one cause of hemorrhoids, but they can all have equally unpleasant outcomes.
Hemorrhoid Symptoms & Characteristics
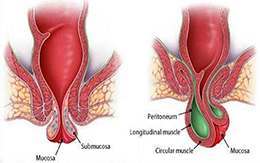
Many people do not experience strong symptoms from internal hemorrhoids. Bloody stools or blood in the toilet bowl can signal the presence of internal hemorrhoids, and these are not always very painful. However, they can grow from the inside to the surface tissue around the anus, causing pain.
The anal bump from the initial external hemorrhoid can further grow and become even more uncomfortable if a blood clot forms, which is called a thrombosed external hemorrhoid. In many cases, hemorrhoid sufferers will rub the irritated bump or attempt to clean it more than usual, which can cause further itching and bleeding. This can actually make the hemorrhoids worse and cause them to last longer and be more painful.
How Does A Doctor Identify Hemorrhoids?
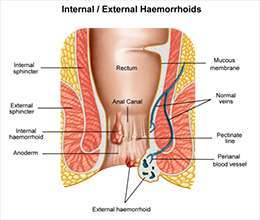
Since rectal bleeding and blood in the stool are the most common symptoms of hemorrhoids, it's important that people experiencing these see a doctor quickly. They can also be symptoms of much more dangerous problems, including certain types of cancer.
Initially, the doctor will simply take a look at the anus and rectum, trying to visually identify swollen vessels (3). They will also perform an exam with a gloved finger.
If necessary, doctors may use an anoscope or proctoscope, both of which are used for viewing the inside of the rectum.
What are Common Hemorrhoid Treatments?
Most hemorrhoid treatment plans are aimed at simply relieving hemorrhoid symptoms, not actually reducing the hemorrhoids themselves. Hemorrhoids are usually temporary, but this course of treatment does not shorten the length of time the sufferer has to deal with them.  Fluids on the surface of the hemorrhoid can further irritate the area, so often patients are advised to take baths in warm water several times a day. Creams and suppositories are common. Dietary changes are also common, with the doctor advising that the patient eat foods with more fiber and drink more water, which will produce larger, softer bowel movements that are easier to pass.
Fluids on the surface of the hemorrhoid can further irritate the area, so often patients are advised to take baths in warm water several times a day. Creams and suppositories are common. Dietary changes are also common, with the doctor advising that the patient eat foods with more fiber and drink more water, which will produce larger, softer bowel movements that are easier to pass.
How to Prevent Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoid prevention hinges on dietary habits that help ease bowel movements. Drinking plenty of fluids and eating foods high in fiber can help prevent hemorrhoids. Wearing looser clothing and avoiding tight underwear can also reduce strain on the anal area. Increasing the amount of exercise you partake in will also benefit you greatly.
References:
2 - American Gastroenterology Association
3 - Mayo Clinic







 HemClear™'s formulation of effective ingredients and strong name recognition have brought praise from both customers and health professionals alike. To learn more about the research and data behind HemClear™ , please visit our "
HemClear™'s formulation of effective ingredients and strong name recognition have brought praise from both customers and health professionals alike. To learn more about the research and data behind HemClear™ , please visit our "




